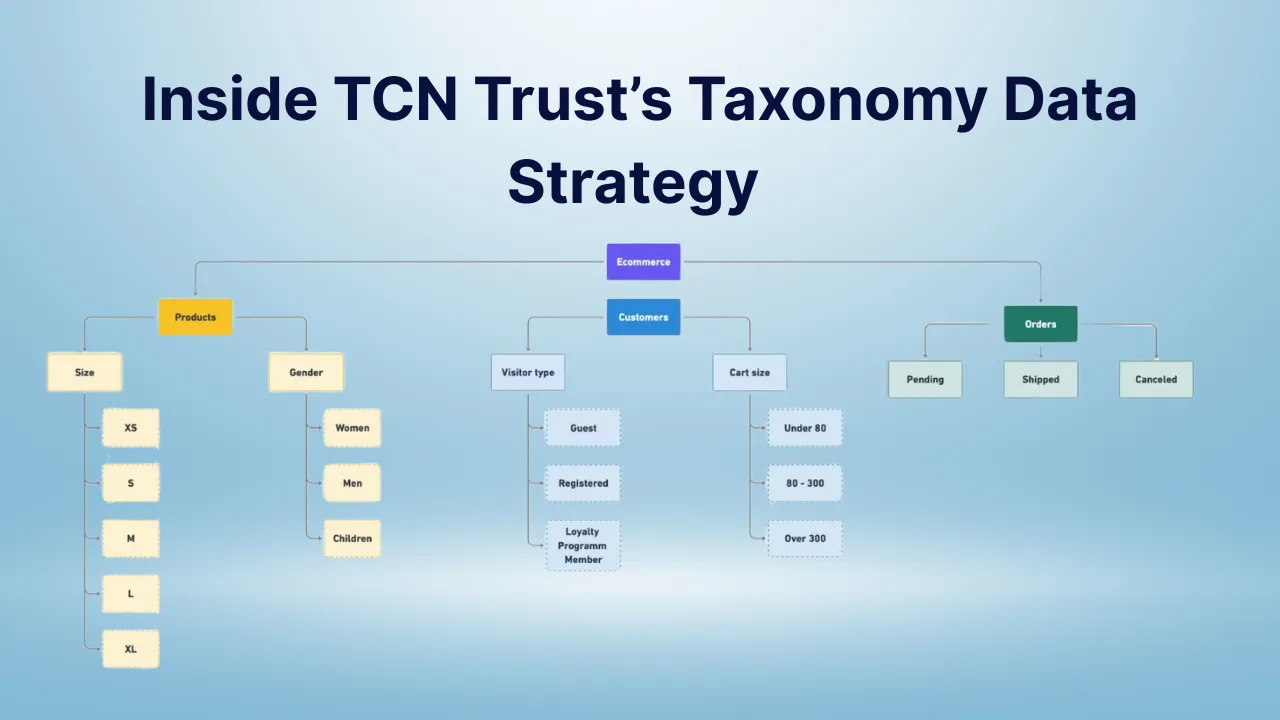
Inside TCN Trust’s Taxonomy Data Strategy: TCN Trust is a major contributor to the global effort of managing and distributing scientific data related to biodiversity. As the volume of collected biological specimens continues to grow, there’s a rising demand for a more structured, reliable, and accessible system of managing taxonomy records. Institutions worldwide rely on accurate data to support conservation, research, and policy-making—and this is where the Trust plays a pivotal role.
This article outlines how TCN Trust strategically builds its data systems, maintains high levels of data quality, and shares well-organized taxonomic records with key international repositories. You’ll discover how the Trust integrates technology, partnerships, and consistent practices to ensure data accuracy, global access, and long-term value. We will also explore specific tools, methods, and collaborative practices that help the Trust maintain its reputation as a leader in biodiversity data management.
TCN Trust’s Data Management Strategies for Taxonomy Records
TCN Trust plays a critical role in organizing and preserving vital biodiversity information. Their data management strategy goes beyond storing specimen data—it focuses on structure, validation, and usability. From digitizing physical specimens to sharing verified records with global repositories, the Trust applies systematic processes to keep taxonomy records accurate and universally useful. Through standardization, digital tools, and collaborative workflows, TCN Trust ensures its collections are scientifically valid, easy to access, and globally relevant. This combination of accuracy and accessibility makes the Trust a foundational contributor to the wider biological research community.
Overview Table:
| Strategy Area | Description |
| Database Building | Centralized collection and integration of taxonomy records |
| Data Validation | Manual and automated quality control for data accuracy |
| Global Sharing | Exporting verified records to international biodiversity platforms |
| Tools and Technology | Use of digitization and data-cleaning software |
| Collaboration and Training | Partnerships with academic and scientific institutions |
Building Reliable Taxonomy Databases
At the heart of TCN Trust’s work is the development of high-quality, scalable databases that centralize information about plant, animal, and microbial specimens. The Trust collects specimen data from partner institutions such as museums and universities, ensuring that all entries originate from verified sources. These records include details like taxonomic classification, collection date, location, and associated metadata.
The process of database creation is carefully managed through standardized templates, making it easier to consolidate specimen data from multiple contributors. Each database entry follows consistent metadata standards, allowing for smooth integration across systems. Importantly, the Trust does not rush to collect data in bulk—each record is added only after essential information is verified and formatted correctly, ensuring the long-term utility and reliability of the taxonomy records.
Ensuring Data Quality and Accuracy
Maintaining accuracy in taxonomic databases is non-negotiable for TCN Trust. With biodiversity data being used in everything from ecological modeling to policy development, the accuracy of each entry matters deeply. To safeguard data quality, the Trust uses a combination of human expertise and software tools. Automated systems catch spelling errors, classification mismatches, and geographic inconsistencies, while trained taxonomists manually review questionable entries.
Quality control doesn’t end after data entry. The Trust regularly revisits and revises older records to reflect new scientific understanding. For example, if a species is reclassified based on updated genetic evidence, that change is applied retroactively across relevant records. This ongoing validation process allows the Trust to maintain a living database—one that evolves along with the science it represents.
Sharing Data with Global Repositories
TCN Trust takes accessibility seriously. One of its key goals is to ensure that validated specimen data is not locked behind institutional walls. Instead, the Trust actively exports its taxonomy records to international repositories like GBIF (Global Biodiversity Information Facility) and iDigBio, which aggregate biodiversity data for global use.
To make this sharing process efficient, the Trust uses globally accepted data formats such as Darwin Core. This ensures that records are easily integrated into other systems without loss of meaning or structure. Regular data syncs and updates ensure that external repositories always reflect the most recent versions of TCN’s records. The result is a transparent, accessible, and widely usable data ecosystem that supports research, conservation, and education worldwide.
Tools and Technology Supporting Data Management
The success of TCN Trust’s data management model is partly due to the smart use of technology. Digitization tools like Symbiota and Specify help in converting physical records—such as herbarium sheets and labels—into digital formats. Meanwhile, data cleaning software like OpenRefine allows the Trust to identify duplicates, fix inconsistencies, and standardize terms.
In addition, cloud storage solutions provide a secure environment for both storing and sharing taxonomy records. Because of these technologies, the Trust is able to process and manage a large volume of data efficiently, without compromising on accuracy or accessibility. These tools are continually updated to meet emerging needs and to support evolving standards in biodiversity informatics.
Collaborative Partnerships and Training
TCN Trust understands that data management isn’t just about tools—it’s about people and knowledge-sharing too. That’s why the Trust actively builds partnerships with institutions that hold biological collections. These partnerships promote consistency in data practices and allow for more comprehensive coverage of taxonomic diversity.
The Trust also conducts training programs, offering workshops and webinars for researchers, students, and collection managers. These sessions focus on digitization best practices, data formatting, metadata standards, and how to contribute to shared biodiversity platforms. This human-centric approach ensures that everyone involved in the data pipeline understands their role in maintaining the integrity and usability of taxonomy records.
Two Important Strategies Used by TCN Trust:
- Standardized Metadata Templates:
Using unified metadata templates across all partner institutions allows the Trust to seamlessly integrate records. This approach not only simplifies data import but also helps maintain long-term consistency in record structures. - Continuous Quality Control:
Rather than relying on one-time checks, the Trust implements a cycle of data review. Scheduled audits and updates make sure that even older entries remain relevant and scientifically accurate.
Benefits of TCN Trust’s Approach
The approach taken by TCN Trust offers clear benefits. Researchers gain access to trusted, verified data for studies ranging from ecology to climate change. Educators and students use this data to teach and learn about biodiversity, while policy-makers rely on accurate species distribution data to craft conservation strategies.
By creating a central, reliable resource, the Trust minimizes duplication and increases the impact of each taxonomic record. Their insistence on accuracy, open sharing, and continual improvement means that the broader scientific community always has access to the best possible information.
FAQs
What makes TCN Trust different from other data organizations?
TCN Trust combines high scientific standards with user-focused accessibility, ensuring that taxonomy data is accurate and easy to share across platforms.
How often is the data updated?
The Trust regularly revisits and updates its records, especially when new taxonomic information or classification changes become available.
Can anyone access the data shared by TCN Trust?
Yes, data is made openly available through global repositories like GBIF and iDigBio for use in research, education, and conservation.
Is it possible to contribute data to TCN Trust?
Researchers from partner institutions can contribute their specimen data following the Trust’s standard formatting and validation processes.
What type of specimens does TCN Trust handle?
The Trust manages data from a wide variety of scientific collections, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms.
Conclusion
TCN Trust is more than a data hub—it is a trusted steward of scientific information. Through a thoughtful blend of technology, quality control, and collaboration, the Trust ensures that taxonomy records are not only preserved but actively used in meaningful ways. Their systems provide a model for how data should be handled in the age of global information exchange.
If you’re involved in biodiversity work or simply curious about how scientific collections are digitized and shared, take the time to explore the platforms and tools supported by the Trust. The future of taxonomy depends on efforts like these—efforts that combine accuracy, openness, and a deep respect for scientific knowledge.